Obsah stránky je výtahem a překladem vybraných částí kapitol, které jsou uvedeny v následujících originálních publikacích: Ekologie lesa a Closer-to-Nature Forest Management. Doporučené citace uvedených publikací jsou následující:
Rotter, P., & Purchart, L. (2023). Ekologie lesa. Mendelova univerzita v Brně. https://doi.org/10.11118/978-80-7509-927-3.
Larsen, J. B., Angelstam, P., Bauhus, J., Carvalho, J. F., Diaci, J., Dobrowolska, D., Gazda, A., Gustafsson, L., Krumm, F., Knoke, T., Konczal, A., Kuuluvainen, T., Mason, B., Motta, R., Pötzelsberger, E., Rigling, A., & Schuck, A. (2022). Closer-to-Nature Forest Management. https://doi.org/10.36333/fs12.
Ve střední Evropě bývá za hlavní příčinu ohrožení biodiverzity v lesních ekosystémech považováno plošné intenzivní pěstování stejnověkých monokultur komerčních dřevin, zejména smrku ztepilého (Picea abies) a borovice lesní (Pinus sylvestris), těžených holosečným způsobem. Dalšími podstatnými a hospodařením způsobenými faktory jsou nedostatek nejrůznějších forem odumřelé dřevní biomasy (mrtvého dřeva), starých a biotopových stromů, eliminace prostředí světlého lesa a odstraňování tzv. biologického dědictví přirozených disturbancí nahodilými těžbami.
Elisabeth Pötzelsbergerová ve své publikaci (2021) rozlišuje příčiny ohrožení biodiverzity následovně:
a) Externí příčiny (mimo lesní hospodářství)
- klimatické změny,
- fragmentace krajiny,
- atmosférické depozice některých sloučenin (např. reaktivních forem dusíku),
- dálkový úlet pesticidů ze zemědělství,
- poškození zvěří,
- biologické invaze.
b) Interní příčiny (uvnitř lesního hospodářství)
- úbytek starých stromů, porostů (old-growth forests),
- úbytek starobylých lesů (ancient forests),
- opuštění tradičních způsobů hospodaření,
- rostoucí zásoby porostů,
- náhrada původních lesů homogenními (jehličnatými) plantážními lesy,
- intenzifikace těžby biomasy, často spojená s výrobou bioenergie.
Dále uvádíme rozbor příčin ohrožení biodiverzity jako kompilaci rozsáhlého souboru publikací a jejich autorských kolektivů z publikace Closer-to-Nature Forest Management (tabulka 1).
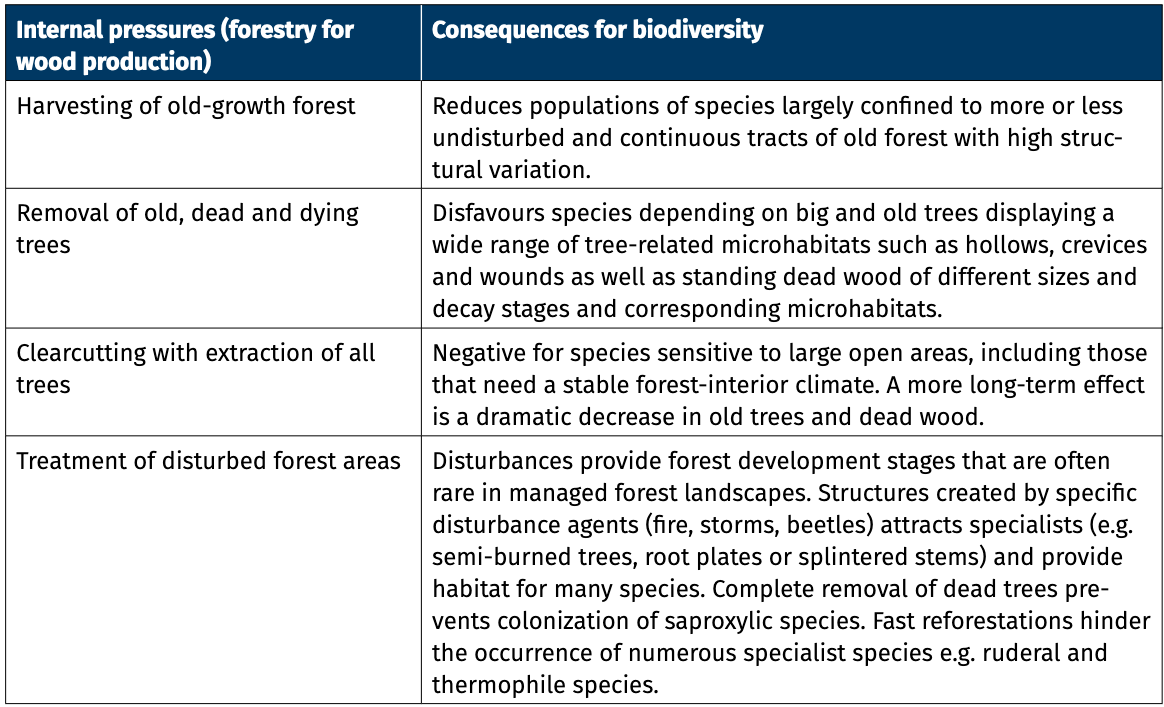
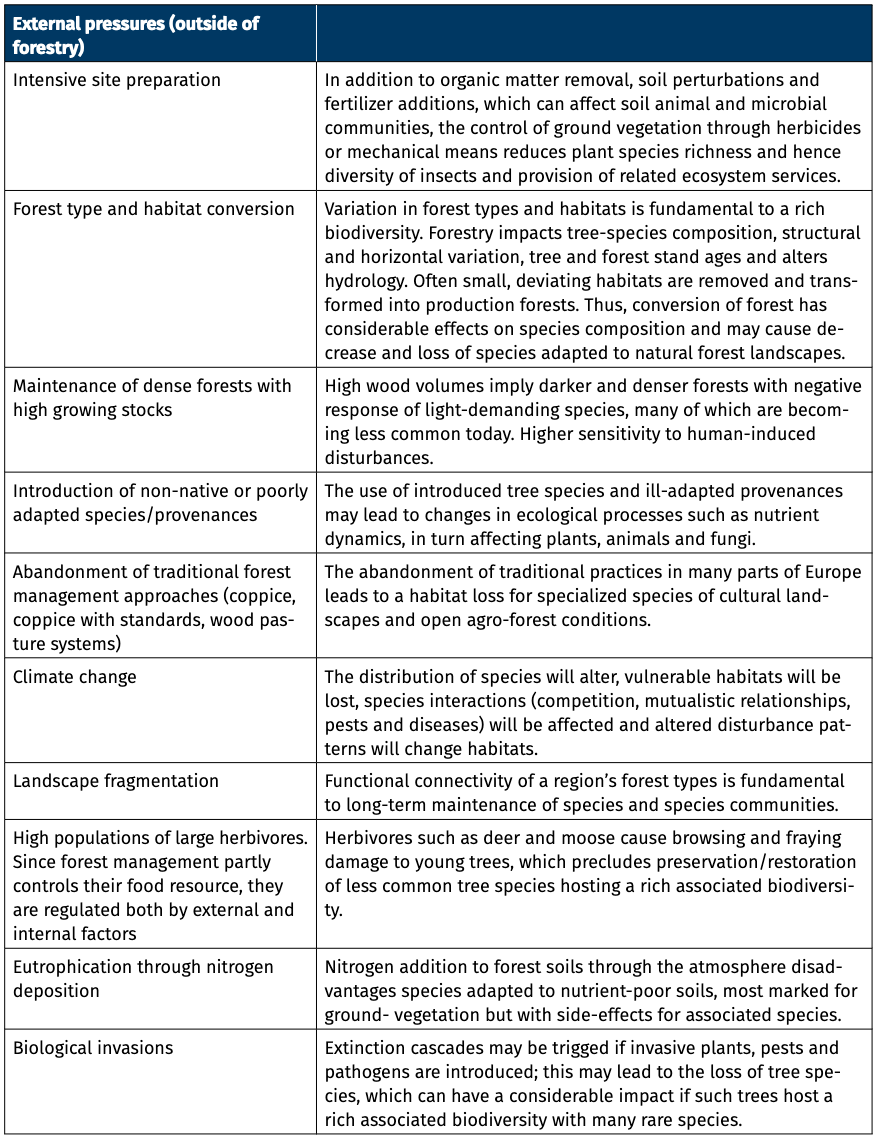 Tab. 1: Hlavní tlaky na biodiverzitu (rostliny, živočichové a houby) způsobené lesním hospodářstvím se zaměřením na produkci dřeva (vnitřní tlaky) a dalšími faktory (vnější tlaky) a jejich důsledky pro biodiverzitu. Literární zdroje, které sloužily jako podklad k tvorbě tabulky: Addison et al. 2019; Bernes et al. 2018; Bernhardt-Römermann et al. 2015; Carpio et al. 2021; EEA 2020; Fahrig 2003; Fedrowitz et al. 2014; Götmark 2013; Gundale 2021; Košulič et al. 2021; Krumm and Vítková 2016; Liebhold et al. 2017; Lindenmayer and Laurance 2017; Lindner et al. 2013; Milad et al. 2011; O’Brien et al. 2021; Plue et al. 2013; Pötzelsberger et al. 2021; Stokland et al. 2012; Thorn et al. 2018, 2020b; Thom and Seidl 2016; Unrau et al. 2018; Verheyen et al. 2012; Vilén et al. 2016.
Tab. 1: Hlavní tlaky na biodiverzitu (rostliny, živočichové a houby) způsobené lesním hospodářstvím se zaměřením na produkci dřeva (vnitřní tlaky) a dalšími faktory (vnější tlaky) a jejich důsledky pro biodiverzitu. Literární zdroje, které sloužily jako podklad k tvorbě tabulky: Addison et al. 2019; Bernes et al. 2018; Bernhardt-Römermann et al. 2015; Carpio et al. 2021; EEA 2020; Fahrig 2003; Fedrowitz et al. 2014; Götmark 2013; Gundale 2021; Košulič et al. 2021; Krumm and Vítková 2016; Liebhold et al. 2017; Lindenmayer and Laurance 2017; Lindner et al. 2013; Milad et al. 2011; O’Brien et al. 2021; Plue et al. 2013; Pötzelsberger et al. 2021; Stokland et al. 2012; Thorn et al. 2018, 2020b; Thom and Seidl 2016; Unrau et al. 2018; Verheyen et al. 2012; Vilén et al. 2016.
Z výše uvedeného je zřejmé, že lesní hospodářství ovlivňuje biodiverzitu mnoha způsoby. Například ovlivněním hustoty a zápoje porostů, množstvím mrtvého dřeva ponechaného v lese, výběrem a směsmi dřevin, délkou rotace a množstvím ponechaných starých stromů apod. Obdobně jako v zemědělství vzniká největší celkový problém v oblastech výrazné intenzifikace využívání lesa a homogenizace struktury a složení lesa. Přesto je bohužel nutné si připustit, že neexistuje žádný univerzální model pro optimální řešení biodiverzity na úrovni krajiny. Heterogenita lesa napříč krajinou je však bezpochyby klíčem k vysoké rozmanitosti druhů.
Citovaná literatura
- Addison, S. L., Smaill, S. J., Garrett, L. G., & Wakelin, S. A., 2019. Effects of forest harvest and fertiliser amendment on soil biodiversity and function can persist for decades. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 135, 194-205.
- Bernes, C., Macura, B., Jonsson, B.G., Junninen, K., Müller, J., Sandström, J., Lõhmus, A., Macdonald, E. 2018. Manipulating ungulate herbivory in temperate and boreal forests: effects on vegetation and invertebrates. A systematic review. Environ Evid 7, 13; https://doi.org/10.1186/s13750-018-0125-3.
- Bernhardt-Römermann, M., Baeten, L., Craven, D., De Frenne, P., Hédl, R., Lenoir, J., … & Verheyen, K., 2015. Drivers of temporal changes in temperate forest plant diversity vary across spatial scales. Global change biology, 21(10), 3726-3737.
- Carpio, A. J., Apollonio, M., & Acevedo, P., 2021. Wild ungulate overabundance in Europe: contexts, causes, monitoring and management recommendations. Mammal Review, 51(1), 95-108.
- Fahrig, L., 2003. Effects of habitat fragmentation on biodiversity. Annual review of ecology, evolution, and systematics, 34(1), 487-515.
- Fedrowitz, K., Koricheva, J., Baker, S.C., Lindenmayer, D.B., Palik, B., Rosenvald, R., Beese, W., Franklin, J.F., Kouki, J., Macdonald, E. and Messier, C., 2014. Can retention forestry help conserve biodiversity? A meta-analysis. Journal of Applied Ecology, 51(6), pp.1669-1679.
- Götmark, F., 2013. Habitat management alternatives for conservation forests in the temperate zone: Review, synthesis, and implications. Forest Ecology and Management, 306, 292-307.
- Gundale, M. J., 2021. The impact of anthropogenic nitrogen deposition on global forests: Negative impacts far exceed the carbon benefits. Global change biology. DOI: 10.1111/gcb.15959.
- Košulič, O., Procházka, J., Tuf, I. H., & Michalko, R., 2021. Intensive site preparation for reforestation wastes multi-trophic biodiversity potential in commercial oak woodlands. Journal of Environmental Management, 300, 113741.
- Krumm, F. and Vítková, L. (eds) 2016. Introduced tree species in European forests: opportunities and challenges. European Forest Institute. 423 pp.
- Liebhold, A. M., Brockerhoff, E. G., Kalisz, S., Nuñez, M. A., Wardle, D. A., & Wingfield, M. J., 2017. Biological invasions in forest ecosystems. Biological Invasions, 19(11), 3437-3458.
- Lindenmayer, D. B., & Laurance, W. F., 2017. The ecology, distribution, conservation and management of large old trees. Biological Reviews, 92(3), 1434-1458.
- Lindner, M., Krumm, F., Nabuurs, G.-J., 2013. Biodiversity conservation and forest management in European forest ecosystems under changing climate. In D. Kraus & F. Krumm (Eds.), Integrative approaches as an opportunity for the conservation of forest biodiversity (pp. 206-215). European Forest Institute.
- Milad, M., Schaich, H., Bürgi, M., & Konold, W., 2011. Climate change and nature conservation in Central European forests: a review of consequences, concepts and challenges. Forest ecology and management, 261(4), 829-843.
- O’Brien, L., Schuck, A., Fraccaroli, C., Pötzelsberger, E., Winkel, G. and Lindner, M., 2021: Protecting old-growth forests in Europe – a review of scientific evidence to inform policy implementation. Final report. European Forest Institute. DOI: https://doi.org/10.36333/rs1.
- Plue, J., Van Gils, B., De Schrijver, A., Peppler-Lisbach, C., Verheyen, K., & Hermy, M., 2013. Forest herb layer response to long-term light deficit along a forest developmental series. Acta oecologica, 53, 63-72.
- Pötzelsberger, E., Bauhus, J., Muys, B., Wunder, S., Bozzano, M., Farsakoglou, A-M., Schuck, A., Lindner, M. and Lapin, K. 2021 Forest biodiversity in the spotlight – what drives change? European Forest Institute. https://efi.int/publications-bank/forest-biodiversity-spotlight-what-drives-change.
- Stokland, J., Siitonen, J., Jonsson, B.G., 2012. Biodiversity in Dead Wood. Cambridge University Press. ISBN: 9780521888738.
- Thorn, S.; Bässler, C.; Burton, P.J.; Cahall, R.E.; Campbell, J.L.; Castro, J.; et al., 2018: Impacts of salvage logging on biodiversity – A meta-analysis. Journal of Applied Ecology 55: 279–289. https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2664.12945.
- Thom, D., Seidl, R., 2016. Natural disturbance impacts on ecosystem services and biodiversity in temperate and boreal forests. Biological reviews of the Cambridge Philosophical Society 91 (3), 760–781. https://doi.org/10.1111/brv.12193.
- Unrau, A., Becker, G., Spinelli, R., Lazdina, D., Magagnotti, N., Nicolescu, V.N., Buckley, P., Bartlett, D., Kofman, P.D. (Eds.) 2018. Coppice Forests in Europe. Freiburg i. Br., Germany: Albert Ludwig University of Freiburg.
- Verheyen, Kris, Lander Baeten, Pieter De Frenne, Markus Bernhardt-Römermann, Jörg Brunet, Johnny Cornelis, Guillaume Decocq et al., 2012. Driving factors behind the eutrophication signal in understorey plant communities of deciduous temperate forests. Journal of Ecology 100, no. 2: 352-365.
- Vilén, T., Cienciala, E., Schelhaas, M. J., Verkerk, P. J., Lindner, M., & Peltola, H., 2016. Increasing carbon sinks in European forests: effects of afforestation and changes in mean growing stock volume. Forestry: An International Journal of Forest Research, 89(1), 82-90.